1. Introduction of waste transformer Oil Distillation Plant
Waste Transformer Oil Distillation Plant ,is the new technology which can refine the waste transformer oil into base oil(which can be made into diesel and gasoline after processed by our catalyst). The oil quality is better than the original normal pressure distillation technology, which show on purity ,transparence, lightness .this technology will do deodorization and destinke process to the raw material oil automatically by "dry type" vacuum pressure distillation method. With the vacuum distillation technology, the distillation temperature is considerably reduced, and the oil output will higher 5%-10% compared with original normal pressure distillation technology. It makes more profits to the enterprise virtually.
2. Raw material which can be used
a. Waste oil .example: waste diesel, waste oil residue etc.
b. tire/rubber oil
c. plastic oil
d. crude oil
e. waste engine oil
f. waste motor oil
g. waste lube oil
h. waste transformer oil
i. underground oil
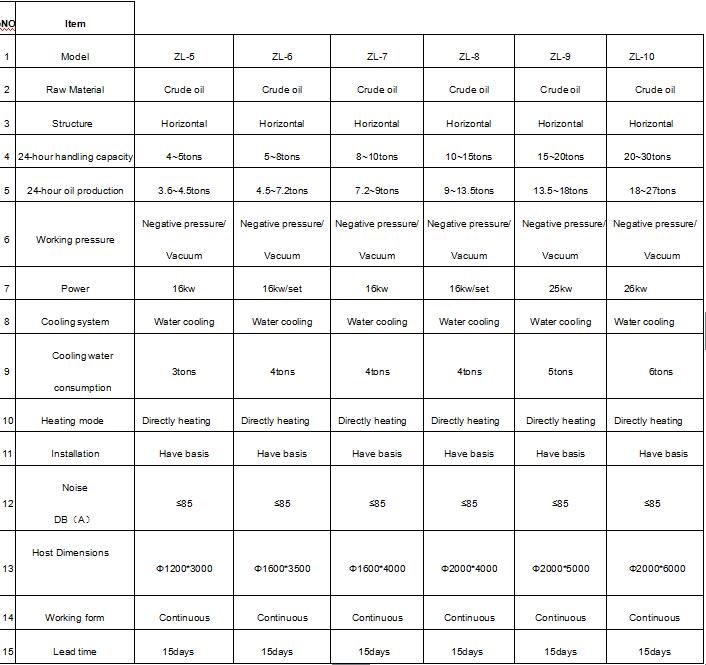
3. Models of waste transformer oil distillation plant
4. Installation: We will be in charge of arranging our engineer to go to your place to guide the installation and train your workers how to operate the waste transformer oil distillation plant ,and buyer will be in charge of the food, accommodation and round air tickets.
5.Waste Transformer Oil Distillation Plant Exporting Experience:
America:
Brazil, Canada, Colombia, USA,
Middle East:
Dubai, Iran, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Turkey
Europe:
Albania , Bosnia and Herzegovina
Asia:
Afghanistan, India, Malaysia, Pakistan, Philippines, South Korea, Vietnam, Myanmar
Africa:
Ghana, Mozambique, Zambia
Waste Transformer Oil Distillation Plant Waste Transformer Oil Distillation Plant,Transformer Oil Waste Oil Distillation Plant,Transformer Oil Refinery Plant,Oil Recycle Distillation Machine Plant Shangqiu Sihai Energy Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.sihaienergy.com
The valve is the control component in the pipeline fluid delivery system and is used to change the passage section and the direction of the medium flow. It has functions such as diversion, cut-off, throttling, non-return, diversion, or pressure relief. Valves for fluid control, ranging from the simplest stop valve to various valves used in highly complex automatic control systems, are available in a wide range of sizes and sizes. The valve's nominal size ranges from extremely small gauge valves up to 10m in diameter. Industrial pipeline valves. It can be used to control the flow of various types of fluids such as water, steam, oil, gas, mud, various corrosive media, liquid metals, and radioactive fluids. The working pressure of the valve can be from ultra high pressure from 0.0013MPa to 1000MPa, and the working temperature can be The c-270°C ultra-low temperature to 1430°C high temperature valve control can use a variety of transmission methods, such as manual, electric, hydraulic, pneumatic, turbo, electromagnetic, electro-hydraulic, electro-hydraulic, gas-liquid, spur gears. , Bevel gear drive, etc.; It can be operated according to predetermined requirements under the action of pressure, temperature or other forms of sensing signals, or it can be simply opened or closed without relying on the sensing signal, and the valve can be opened and closed by means of a drive or an automatic mechanism. The pieces are used for lifting, slipping, swinging or swinging to change the size of the runner area to achieve its control function.
Parts of the cleaning step valve must be processed through the following processes before assembly:
1, according to processing requirements, some parts need to be polished, the surface can not be processed burr;
2, all parts degreasing treatment;
3, after the completion of degreasing pickling passivation, cleaning agent does not contain phosphorus;
4. After pickling, purifying and rinsing with purified water, there can be no residue of the chemicals. The carbon steel parts eliminate this step;
5. One by one component is wiped with a non-woven fabric, and the surface of the components such as wire wool cannot be retained, or it can be blown dry with clean nitrogen;
6. Wipe the individual parts with non-woven cloth or precision filter paper and wipe the pure alcohol until no dirt is found.
Assembly Requirements The cleaned parts must be sealed for installation.
The installation process requires the following:
1. The installation shop must ensure cleanliness, or set up a temporary clean area, such as a newly purchased strip cloth or plastic film, to prevent dust from entering during installation.
2, the assembly workers must wear clean cotton overalls, wearing a cotton cap, hair can not leak, wear clean shoes, wear plastic gloves, degreasing.
3, assembly tools must be degreased before cleaning to ensure clean.
Other requirements 1. The assembled valve is purged with nitrogen for at least 1 minute.
2, airtight test must be pure nitrogen.
3. After the airtight test is qualified, carry out the enclosure, seal it with a clean polyethylene cap, and soak the polyethylene cap with an organic solvent before use.
4. Then seal with a vacuum bag.
5, the last box.
6. Take measures to ensure that the envelope is not damaged during the transportation.
Acceptance requirements Acceptance Acceptance Follow HG20202-2000 “Specifications for Construction and Acceptance of Degreasing Projectsâ€. Before assembly, each component shall be wiped with clean, precision filter paper. Select dead parts of the components and the filter paper shall not pass color as qualified.
Classification according to the role and use (1) cut-off categories: such as gate valves, globe valves, plug valves, ball valves, butterfly valves, needle valves, diaphragm valves and so on.
Truncated valves, also known as closed-circuit valves and globe valves, act to switch on or cut off the medium in the pipeline.
Check valve, also known as check valve or check valve, check valve is an automatic valve, its role is to prevent the back flow of media in the pipeline, to prevent the pump and drive motor reverse, and the leakage of the container medium. The bottom valve of the pump is also a check valve.
Explosion-proof valve, accident valve, etc. The role of the safety valve is to prevent the medium pressure in the pipeline or device from exceeding the specified value, so as to achieve the purpose of safety protection.
Regulating valve, throttle valve and pressure reducing valve, its role is to adjust the pressure, flow and other parameters of the medium.
(2) Vacuum: vacuum ball valve, vacuum flapper valve, vacuum inflation valve, pneumatic vacuum valve, etc. Its role is in the vacuum system, used to change the direction of the gas flow, adjust the size of the gas flow, cut off or connect the vacuum system components called the vacuum valve.
(3) Special-purpose categories: such as pigging valves, vent valves, drain valves, exhaust valves, filters, etc.
The exhaust valve is an essential auxiliary component in the pipeline system and is widely used in boilers, air conditioners, oil and gas, and water supply and drainage pipelines. It is often installed at high points or elbows, eliminates excess gas in pipelines, improves the efficiency of pipeline usage, and reduces energy consumption.
According to the main parameters according to the nominal pressure (1) vacuum valve: refers to the valve working pressure is lower than the standard pressure.
(2) Low pressure valve: refers to the valve with nominal pressure PN ≤ 1.6Mpa.
(3) Medium pressure valve: refers to the valve with nominal pressure PN of 2.5Mpa, 4.0Mpa, and 6.4Mpa.
(4) High pressure valve: It refers to the valve with the nominal pressure PN of 10.0Mpa to 80.0Mpa.
(5) Ultra-high pressure valve: It refers to the valve with nominal pressure PN≥100.0Mpa.
According to the working temperature (1) ultra-low temperature valve: for the media operating temperature t <- 101 °C valve.
(2) Normal temperature valve: used for medium working temperature -29°C
(3) Medium temperature valve: used for medium working temperature 120°C
(4) High temperature valve: used for valves with medium working temperature t>425°C.
According to the driving mode, it is divided into automatic valve type, power driven valve type and manual valve type compressed air driven valves according to the driving mode. Hydraulic valve: Valve driven by liquid pressure, such as oil.
In addition there are several combinations of driving methods such as gas-electric valves.
According to the nominal diameter (1) small diameter valve: nominal diameter DN ≤ 40mm valve.
(2) Medium-diameter valves: Valves with a nominal diameter DN of 50 to 300mm.
(3) Large-diameter valves: Valves with a nominal valve DN of 350 to 1200 mm.
(4) Extra large diameter valve: valve with nominal diameter DN ≥ ≥ 1400mm According to structural characteristics Valve structural characteristics Valve structural characteristics The structural characteristics of the valve are divided according to the direction of movement of the closure relative to the valve seat:
(1) Cut gate shape: The closure moves along the center of the valve seat; for example, the stop valve (2) is a plug and a ball: the closing part is a plunger or a ball and rotates around its own centerline; for example, a plug valve, a ball valve (3) gate Shape: The closure moves along the center of the vertical seat; such as gate valves, gates, etc. (4) Swivel shape: The closure rotates around the axis outside the valve seat; for example, a swing check valve, etc. (5) Butterfly: Closed part The disc rotates around the axis in the valve seat; for example, butterfly valve, butterfly check valve, etc. (6) Slide valve shape: The closing member slides in the direction perpendicular to the channel. Such as sliding connection method (1) threaded connection valve: valve body with internal thread or external thread, and pipe thread..
(2) Flange connection valve: The valve body has a flange and is connected with the pipe flange.
(3) Welding connection valve: The valve body has a welding groove and is welded to the pipe.
(4) Clamp connection valve: The valve body has a clamp and is connected to the pipe clamp.
(5) Sleeve connection valve: It is connected with the pipe sleeve.
(6) Coupling valve: The connection form that directly connects the valve and the two pipes together by bolts.
According to valve body material (1) Metal material valve: Its valve body and other parts are made of metal material. Such as cast iron valves, cast steel valves, alloy steel valves, copper alloy valves, aluminum alloy valves, lead alloy valves, titanium valves, Monel alloy valves.
(2) Non-metallic valve: Its valve body and other parts are made of non-metallic materials. Such as plastic valves, enamel valves, ceramic valves, FRP valves.
The following are several stainless steel valve material parameters and specific applications (1) angular stroke, including ball valves, butterfly valves, plug valves and other classification (2) straight trip including gate valve, globe valve, angle seat valve and so on.
This classification method is divided into principles, roles, and structures. It is currently the most commonly used classification method at home and abroad. General sub-gate valve, globe valve, throttle valve, instrument valve, plunger valve, diaphragm valve, plug valve, ball valve, butterfly valve, check valve, relief valve safety valve, steam trap, regulating valve, foot valve, filter, Sewage valve and so on.
Because the valve is widely used, its role is also very large. For example, in a power plant, valves can control the operation of boilers and steam turbines. In petroleum and chemical production, valves also play a role in controlling the normal operation of all production equipment and process flow. The same is true in other sectors. In spite of this, valves are often neglected compared to other products. For example: When installing machinery and equipment, people tend to focus on the main machinery and equipment but ignore the valves. This will reduce the overall production efficiency or stop production, or cause a variety of other accidents. Therefore, the selection, installation, and use of the valve must be carried out in a responsible and responsible manner.
The electric drive valve is a commonly used drive valve. Usually, the drive device in the form of the drive device is a valve electric device. The characteristics of the valve electric device are as follows: 1) The rapid opening and closing can greatly shorten the time needed to open and close the valve; 2) can greatly reduce the operator's labor intensity, especially suitable for high pressure, large diameter valve; 3) is suitable for installation in the position can not be manually operated or difficult to access, easy to achieve long-range operation, and the installation height is not limited; 4 ) It is beneficial to the automation of the whole system; 5) The power source is easier to obtain than the gas source and the liquid source, and the laying and maintenance of the electric wire are also much simpler than the compressed air and the hydraulic pipeline.
The disadvantage of the valve electric device is that it is complex in construction and it is more difficult to use it in a wet place. When it is used in explosive media, explosion-proof measures are needed.
Valve definition and classification
The valve is a device in the fluid system. The device for controlling the direction, pressure, and flow of the fluid is a device that allows the flow and stoppage of the medium (liquid, gas, powder) in the piping and equipment and can control its flow.